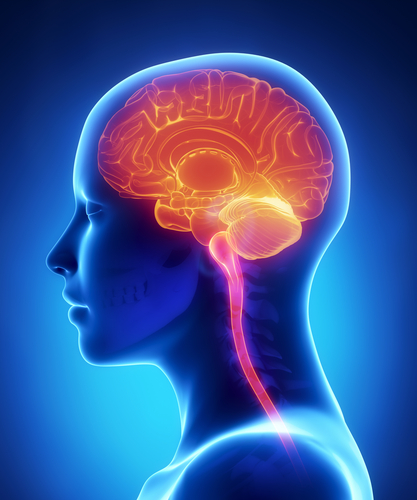
Symptoms of PTSD after mild traumatic brain injury can be difficult to diagnose. Although the presence of brain damage may indicate a psychiatric disorder, the disorder itself is mild. A patient can be affected by PTSD in several ways. The most common symptoms include nightmares, flashbacks, and nightmare-like behavior. The severity of the traumatic event and the duration of its aftermath are factors that determine the severity of PTSD.
While the onset of PTSD symptoms differs from person to person, symptoms of the disorder are typically similar. In some cases, the patient experiences hyperarousal and intrusive thoughts. In other cases, the patient experiences flashbacks. Because PTSD and TBI are both altered brain functions, co-existing conditions complicate treatment and increase the risk of recurrence. Additionally, concussions increase the risk for PTSD.
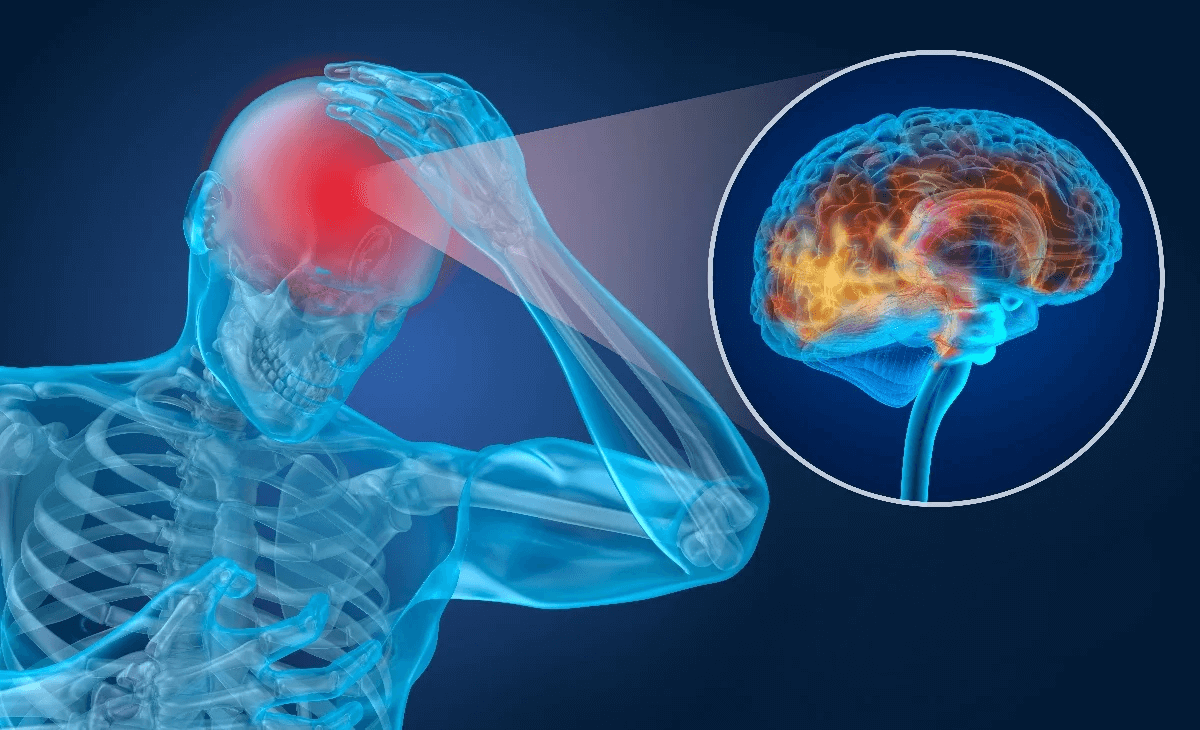
Some patients also experience a loss of memory, which serves as a protective factor against PTSD. The memory loss associated with a mild traumatic brain injury is often accompanied by the development of PTSD. It is common for a patient to avoid social interaction after a TBI because they do not want to have a recurrence of the traumatic event. In some cases, the loss of social interactions can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
The recurrence of traumatic memories can occur despite an altered level of consciousness. While TBI can impair the patient's ability to remember the event in a particular way, they have a memory for it, which helps them adapt to the new environment. A TBI can cause a loss of social relationships. Therefore, the recurrence of traumatic memories in such a situation can result in PTSD.
Besides the mental aspect, TBI can cause emotional lability. People with a mild traumatic brain injury may experience changes in their emotions and give the impression that they are mentally ill. Moreover, PTSD sufferers may develop a heightened sensitivity to fear and may become defensive around other people. Hence, it is important to recognize the difference between a traumatic and a mild traumatic brain injury when evaluating the symptoms of the condition.
Symptoms of PTSD associated with a mild traumatic head injury can be difficult to recognize. Some studies suggest that the severity of the problem is dependent on the nature of the trauma. There is little research on the symptomatology of posttraumatic stress in auto collisions. The effects of PTSD are typically limited to the symptoms of neck pain. Nevertheless, they can make the recovery process difficult.
Symptoms of PTSD associated with a mild traumatic head injury vary depending on the severity of the injury. The severity of the accident, in which the traumatic event occurred, is the strongest predictor of the onset of PTSD. Other factors that may be relevant include the nature of the TBI, the extent of the TBI, and the nature of the trauma. If an individual has a mild traumatic brain injury, the chances of developing PTSD are higher.
Other symptoms of PTSD associated with a mild traumatic body injury can be difficult to identify. Despite the common characteristics of both traumatic brain injuries, it is difficult to distinguish between the two conditions. Changes in cognition, fatigue, and irritability are common signs. Many patients with PTSD also report difficulties with sleep. In some cases, a patient's temper may become short and frustrated, and they may even act out aggressively.
Previously, researchers believed that a mild TBI rarely causes PTSD. However, they now acknowledge that mild TBI is a risk factor for PTSD. While the scientific community previously believed that MTBI did not cause PTSD, they are now aware that it increases the likelihood of a patient suffering from the disorder. While a person who has a mild traumatic brain injury is at almost equal risk for PTSD than someone who has sustained a severe TBI.